Lab Report
Variables: The independent variable is the temperature of the water. The dependent variable is the strength of the hurricane. The control is that they all form over salt water.
Hypothesis: Because hurricanes are powered by thermal energy that is released when water vapor condenses, I hypothesize that the higher the temperature of the ocean where the hurricane reaches its strongest point, the stronger the hurricane will be.
Materials:
· Computer with internet and spreadsheet program(like excel)
· Printer or word processing program (like word)
Procedures:
1. Open a new spreadsheet in excel or a similar program.
2. In the first row, type “Name”, “Temperature of Ocean (°C)”, and “Strength (Saffir-Simpson)”, each in a separate box.
3. Go to http://weather.unisys.com/hurricane/atlantic/ and select 2008.
4. Type in all of the hurricanes listed for that year under “Name” in the spreadsheet along with their strengths.
5. Scroll down to "Individual Storm Details".
6. Click on the maps of the hurricanes you typed in the spreadsheet to see a larger map. Print this out or, to save paper, you can copy and paste the maps in to a word processing program.
7. Go back to the page you were on in step five and click on “tracking information” for each of the hurricanes in the spreadsheet, which will lead you to a data table. Either print this table or copy and paste it into a word processing program.
8. On each of the tables, search the WIND and PR columns to find the entry where the hurricane was at its maximum strength (highest winds, lowest pressure) and highlight the row. Find this position on the map using the ADV columns.
9. Go to http://www.ndbc.noaa.gov/ .
10. Start with Hurricane Bertha.
11. Look at the map you have printed or copied. Find the buoy closest to where the point you found in step 9. The closest one to Bertha’s point is station 41670. Click on it.
12. Click “View History”.
13. Click 2008 on a row under “Standard Meteorological”. (Once you get to the data table, see if this is the right one. If there are nines everywhere, that means that data is missing. Also, not all of them include every month. If it doesn’t work, pick another table.
14. Select “Method 2”.
15. Look for the date and time on the same row of your data table as the point you found in step 9. (Bertha: 07/08/00Z)
16. Find this on the huge data table you just opened.
17. Look in the WTMP (Water Temperature) column for the number that applies to this row. You have finally found the water temperature! Type this into your spreadsheet.
18. Repeat steps 12-19 with the rest of your hurricanes.
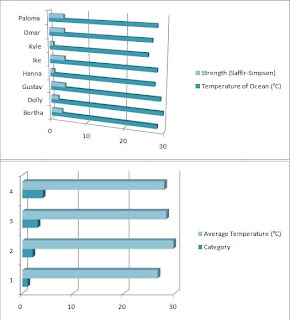
19. Use this data to make a table of averages.
Column 1: Category
Column 2: Average Temperature (°C)
20. Using the program, make a bar graph with the second and third columns of the first table and another using the entire second table.
21. View this article: http://www.commondreams.org/headlines06/0317-08.htm
Because of the data collected in this experiment and the article presented in this report, I claim that the temperature of the water does contribute to the strength of the hurricane. I can prove this statement because of my data and the results of the experiment presented in the article. Because there are four factors to the strength of a hurricane: rising sea surface temperature, humidity in the troposphere, wind shear, and air circulation patterns known as “zonal stretching deformations”, my data still supports this theory. The fact that temperature is not the only factor in hurricane strength also supports the data I collected.
Conclusion:
The purpose of this experiment was to find out if the temperature of the water over which a hurricane travels affects the Saffir-Simpson strength of the hurricane. My hypothesis was that because hurricanes are powered by thermal energy released when water vapor condenses, the higher the temperature of the ocean where the hurricane reaches its strongest point, the stronger the hurricane will be. My hypothesis was correct, but I also discovered that there are three other causes: humidity in the troposphere, wind shear, and air circulation patterns known as “zonal stretching deformations”. I can prove that my hypothesis was correct because category 1 hurricanes had a lower average temperature (26.6) than category 4 hurricanes (27.9). Though the other two categories did not follow this layout, it can be credited to the fact that temperature isn’t the only factor and that there was only one hurricane in each of those categories in the year 2008.
New Questions:
Are hurricanes that form closer to the equator stronger than hurricanes that form farther away because of increased or decreased ocean temperature?
Coming Soon...
In the next couple of days, the final results of the experiment I have been formulating are going to be posted here. It will be possibly the longest blog post ever written, and I will try to provide links or possibly PDFs for a printable version. Note: If you want to try this experiment, please be aware that it is time-consuming and fairly difficult, but I do not want to discourage you from trying it. I have enjoyed this blog so much and can't wait for you too see the experiment! Also, please note that comments (positive/constructive, please) would be greatly appreciated. Keep reading! Thanks.
Ike Aftermath Video
Note: I did not take this video. The publisher of this video on YouTube is TornadoVideosdotnet.
Parts of a Hurricane
Ever wondered what the parts of a hurricane are? Probably not, but it's good to know, anyway.
The Eye-
Well, you see, a hurricane has to see where it is going, so using a structure similar to a human eye, it... okay, just kidding. The eye is to the hurricane as the inner core is to the Earth (try and figure out the analogy...). Got it? Yes, it means that the eye is in the center of the hurricane. This is also the calmest area of the hurricane. It is usually around twenty miles long.
The Eye Wall-
This is a ring of thunderstorms about 15 miles wide around the eye. It is the opposite of the eye (in terms of calmness), since it is the most destructive part of the storm.
Spiral Rain Bands-
They are curved bands of clouds that move away in a spiral movement, and also bands of thunderstorms that circulate outward from the eye.
These are the basic parts of a hurricane.
Hurricane Katrina
Can't see the video?
Go to:http://www.onetruemedia.com/sharedp=a0f9428473fac238e0cc86&skin_id=701
Hurricane Katrina Stats:
- It was the costliest and one of the five deadliest hurricanes in U.S. history.
- It was the sixth strongest Atlantic hurricane overall.
- At least 1,836 people died in the hurricane.
Hurricane Ike
Can't see the video? Go to:
http://www.onetruemedia.com/shared?p=a0e1d5c1fec6a38c5d3def&skin_id=701
Hurricane Ike Facts:
- Hurricane Ike was the largest hurricane ever observed in the Atlantic basin.
- It was the third most destructive hurricane to make landfall in the United States.
- It started as a tropical disturbance near Africa in late August, 2008.
- On September 1, 2008, it became a tropical storm west of the Cape Verde islands.
- By September 4, 2008, it was a Category 4 hurricane with maximum sustained winds of 145 mph (230 km/h), making it the most intense Atlantic storm of 2008.
- On September 7, it passed the Turks and Caicos Islands as a Category four hurricane with maximum wind speeds of 135 mph(217km/h).
- It passed through Cuba as a Category 4 hurricane (September 7) and then as a Category 1 hurricane (September 9).
- Though Ike made its final landfall over Galveston, Texas as a Category 2 hurricane, its storm surge was equivalent to that of a Category 5 storm.
- Ike was blamed for at least 195 deaths.
- The storm caused millions of dollars worth of damage in many areas.
- It was the cause of the biggest evacuation in Texas history and the biggest search-and-rescue operation in U.S. history.
- On Grand Turk Island, 95% of the homes were damaged.



